How to Download Github Repository Then Upload
Learning Objectives
Later completing this folio, yous will be able to:
- Explain how a GitHub repository stores and tracks changes to files.
- Create a copy of (i.e.
fork) other users' files on GitHub.com . - Use the
git clonecommand to download a copy of a GitHub repository to your computer.
Almost Git and GitHub
Previously in this textbook, you learned that git is tool that is used to track changes in files (a process chosen version command) through a suite of commands that you tin execute in the Terminal. Y'all besides learned that GitHub allows you to shop files in the cloud to admission them from any computer and to share them with others.
Yous tin use git and GitHub together in a workflow to make changes to files locally with git and to store and share your files on GitHub.com. To work together, git and GitHub utilise repositories (i.eastward. directories of files) to manage and store files.
Information Tip: A GitHub repository is a directory of files and folders that is hosted on GitHub.com.
Having a re-create of a prepare of files stored in GitHub repositories in the cloud is ideal considering:
- In that location is a fill-in: If something happens to your calculator, the files are still available online.
- You can share the files with other people easily.
- You tin can even create a Digital Object Identifier (DOI) using third political party tools like Zenodo to cite your files or ask others to cite your files. You tin also add these DOIs to your resume or C.V. to promote your work.
Directory Construction of Repositories
In essence, a repository is a directory for a specific project that is identified equally a repository by git and GitHub because it contains a subdirectory chosen .git.
The .git subdirectory is created automatically, either by GitHub if it is created on GitHub.com or by git if the repository is created locally on a estimator showtime (i.due east. initialized every bit a repository). This .git subdirectory is used past these tools to manage and track the diverse tasks that are run on this directory (due east.g. tracking changes to files in the repository). Thus, you never need to access or modify the files in the .git subdirectory.
A typical repository (e.one thousand. project-name) is structured as follows:
projection-proper noun .git/ data/ scripts/ .gitignore README.physician In addition to the .git subdirectory, it is mutual to take subdirectories for specific files of a workflow such every bit data or scripts. A few common files in most if not all git repos are:
-
README.docfile: This is a Markdown file that is used to provide a description of the repository (i.e. its contents, purpose, etc), so that others can learn how to use the files in the repository. -
.gitignorefile: This file can be used to list the files that y'all practise not want git to track (i.e. monitor via version control). Yous volition larn more well-nigh both of these useful files after in this chapter.
URL of Repositories on GitHub.com
When a repository is stored on GitHub.com, information technology is assigned a unique URL (i.e. link on the GitHub.com website) that can be used to detect the repository and access its files. While repositories on GitHub.com can be fabricated either public or private, the default is public for complimentary GitHub accounts.
In either case (public or private), the URL links to a GitHub repository always follows the aforementioned format:
https://github.com/username/repository-name
The username is the username of the creator (i.e. owner) of the repository. The username can either exist an individual such as eastudent (or your GitHub username!), or it can stand for an organisation such as earthlab-pedagogy.
For example, the repositories that you will work with throughout this textbook will exist endemic past earthlab-education, and thus, volition have URLs that wait similar this:
https://github.com/earthlab-education/repository-name
Using GitHub.com, yous tin brand a copy of a GitHub repository (besides known as a repo) owned past another user or organization (a task referred to every bit forking a repository). This means that y'all do not accept to fork a repository that yous already own. Instead, other users tin fork your repository if they would like a copy to work with, and your original files volition not be modified!
The ability to fork a repository is a benefit of using GitHub repositories because the forked repository is linked to the original. This ways that you (or other users) tin can update the files in your fork from the original to your (or their) forked repository. It also ways that you lot tin can advise changes to the original repository, which can be reviewed by the possessor of that repository. Thus, forking allows yous to interact with others while protecting the original versions of files. When collaborating, everyone will work with copies of the original files. And all changes are tracked in each file'south history and can be undone at any fourth dimension.
You can fork an existing GitHub repository from the main GitHub.com page of the repository that you want to copy.
To fork a repo:
- Navigate to the repo page that you wish to fork - example:
https://github.com/earthlab-education/practice-git-skillz
- On that folio, you will run into a button in the UPPER RIGHT hand corner that says
Fork. The number side by side to that button tells you lot how many times the repo has already been forked. - Click on the
Forkbutton and select your user account when it asks you where yous want to fork the repo. - Once y'all have forked the repo, you will have a copy of it in your business relationship. Navigate to your repo page. The url should wait something like this:
https://github.com/your-user-proper noun/do-git-skillz
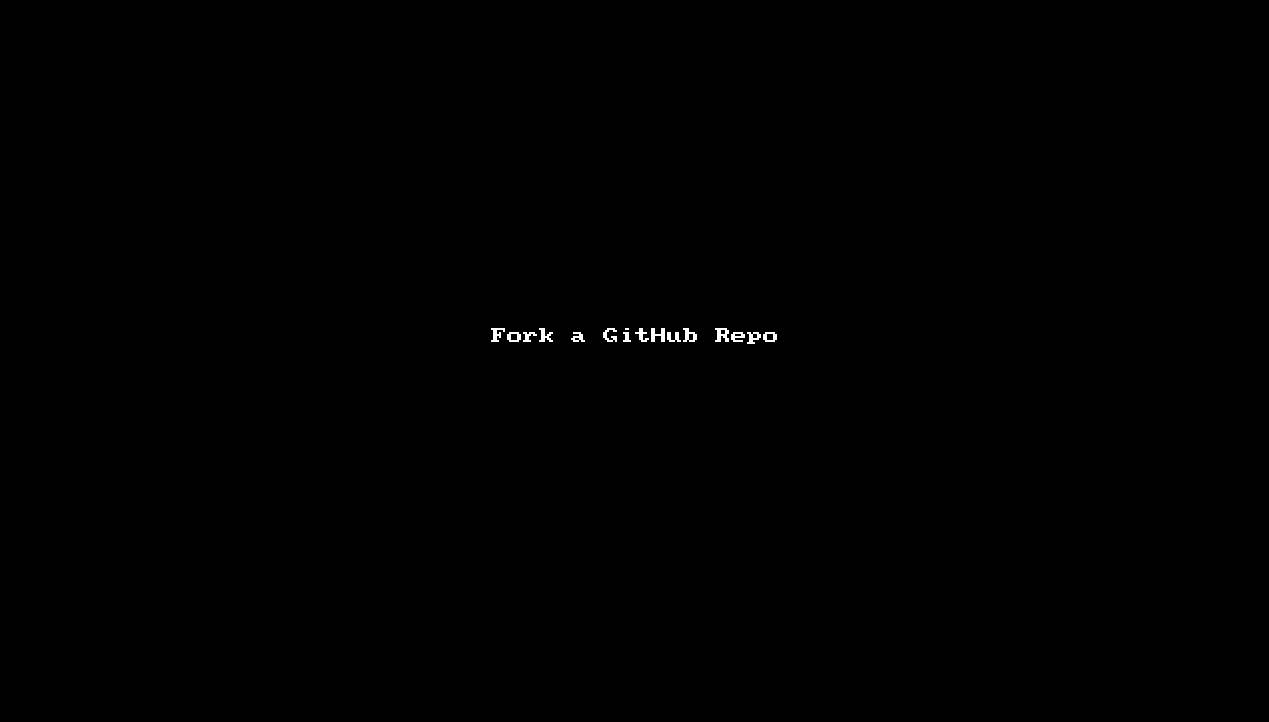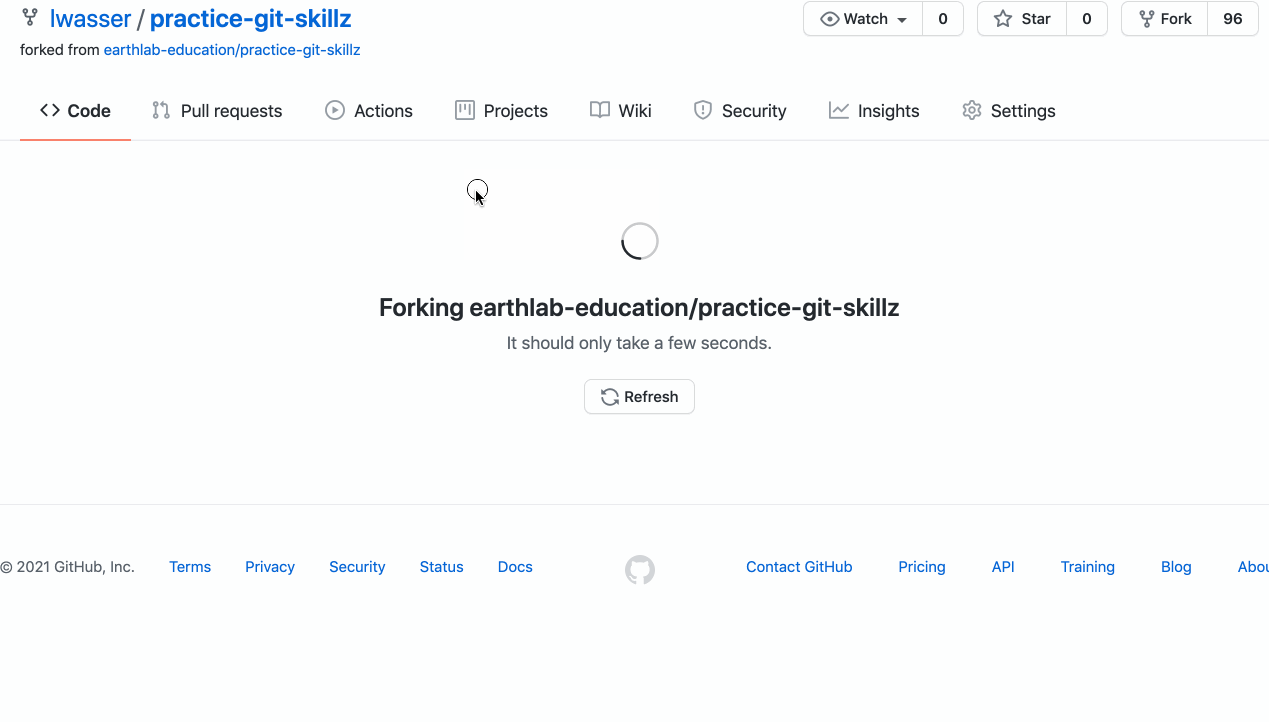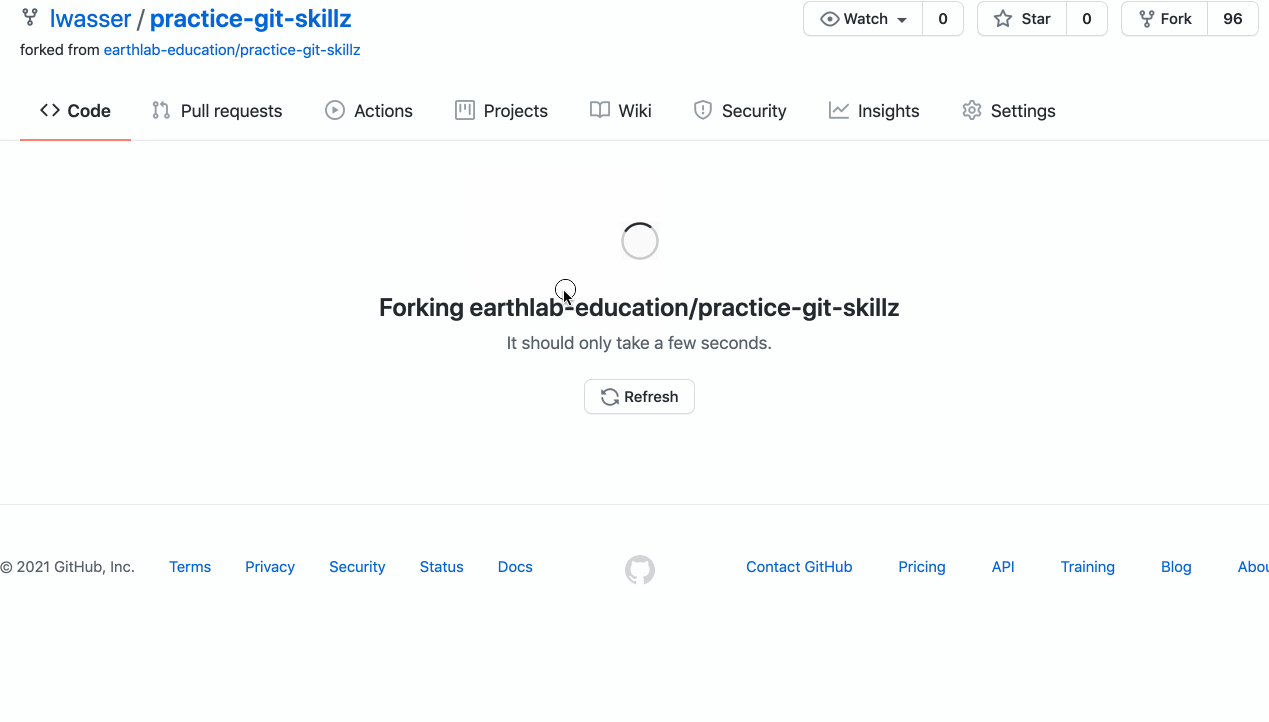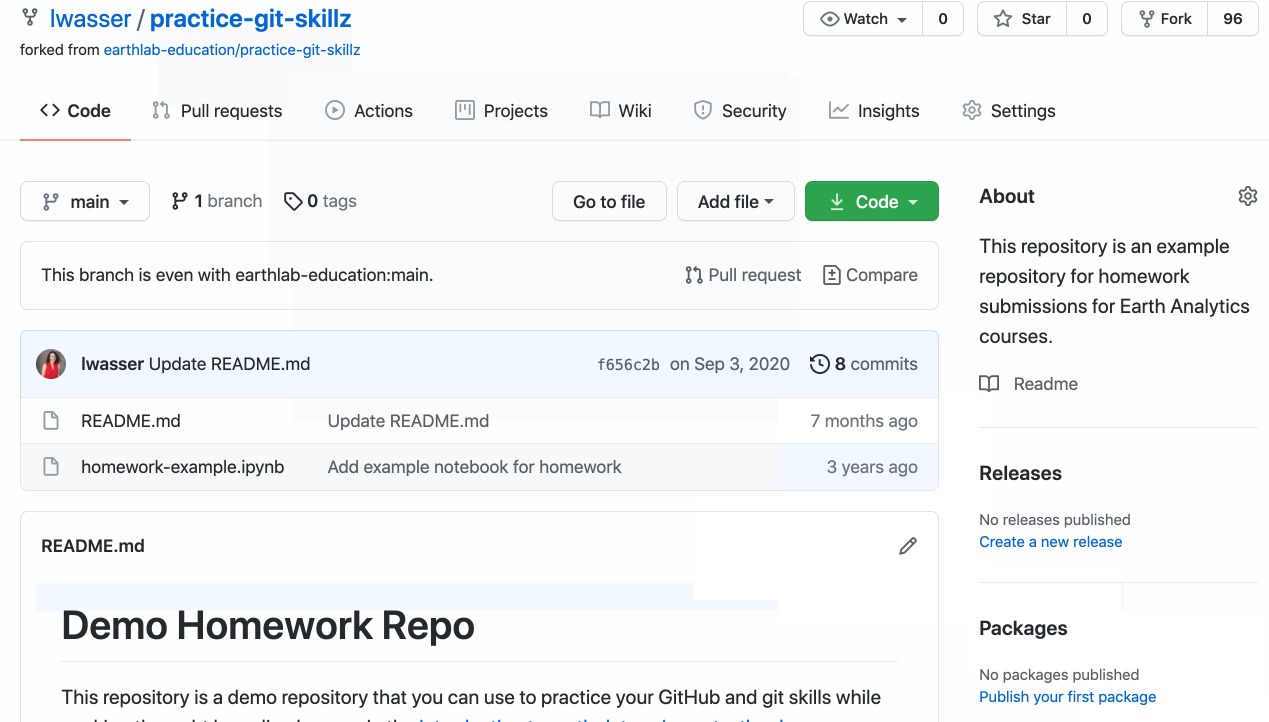
Later on in this textbook, y'all will learn how to suggest changes to the original repository, receive updates from the original repository to your fork, and interact with others.
To work locally with a GitHub repository (including forked repos), you need to create a local copy of that repository on your figurer (a task referred to as cloning a repo). You can clone GitHub repositories that yous own or that are owned by others (e.g. repositories that you have forked to your GitHub account).
In either case, cloning allows you to create a local copy of a GitHub repository, so that yous can work with the files locally on your figurer. Cloning a repository to your computer is a great way to piece of work on your files locally, while still having a copy of your files on the cloud on GitHub.com. Following the steps beneath, yous will use the git clone control in the final to clone GitHub repositories.
Use Fustigate to Change to Your Desired Working Directory
The first step to using any git command is to change the electric current working directory to your desired directory. In the instance of git clone, the current working directory needs to be where you lot want to download a local copy of a GitHub repository.
For this textbook, you will clone a repo into a directory called world-analytics on your computer (or wherever you are working. This globe-analytics directory should be located in the home directory of your computer.
# This command with change your directory to home (`~`) /earth-analytics # If the directory doesn't already exist yous tin brand information technology using mkdir ~/world-analytics $ cd ~/world-analytics $ pwd /users/your-user-name/earth-analytics Copy a Github.com Repository URL From GitHub.com
To run the git clone command, you need the URL for the repository that y'all want to clone (i.e. either a repository owned by you or a fork that you created of another user's repository).
On the main GitHub.com folio of the repository, you lot can click on the green button for Clone or download, and copy the URL provided in the box, which will look similar:
https://github.com/your-username/practice-git-skillz
Data Tip: You can as well copy the URL straight from your web browser, or in some cases, you might already know the URL. Withal, in many cases, yous will come across a new GitHub.com repository on your own and will need to follow these instructions to copy the URL for future use.
Run the Git Clone Command in the Concluding
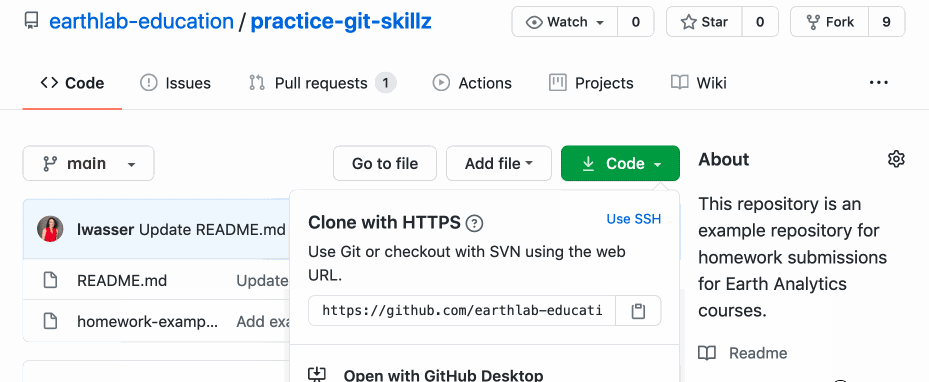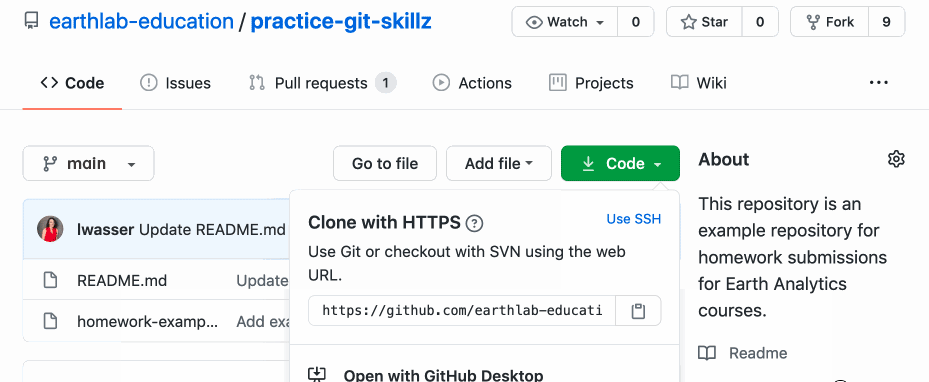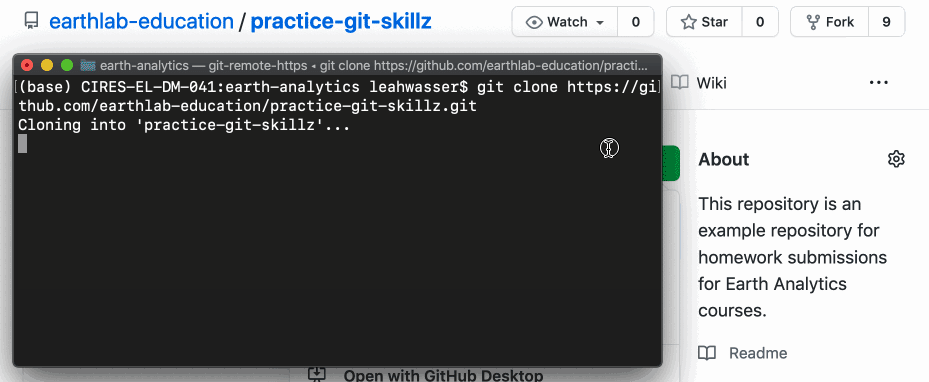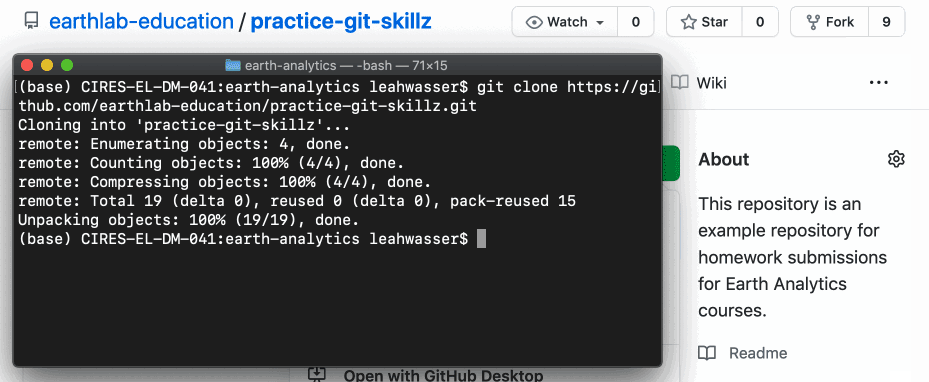
At present that you have the URL for a repository that y'all desire to copy locally, y'all can use the terminal to run the git clone command followed past the URL that you copied:
git clone https://github.com/your-username/exercise-git-skillz You have now made a local copy of a repository nether your globe-analytics directory. You can double cheque that the directory exists using the ls command in the last.
Challenge - Fork and Clone a Repository
Get to GitHub.com and login. Then use the link beneath to open up the exercise-git-skillz repo.
https://github.com/earthlab-education/practice-git-skillz
- On the master GitHub.com page of this repository, you volition come across a button on the top right that says
Fork. The number next toForktells the number of times that the repository has been copied or forked. - Click on the
Forkpush and select your GitHub.com account equally the home of the forked repository. - Once you have forked a repository, you will have a copy (or a fork) of that repository in your GitHub account. The URL to your fork will contain your username:
https://github.com/your-username/practice-git-skillz
- Finally, clone the fork that you lot created above then you accept a copy of all the files on github.com on your local computer. You may want to clone this repo into your globe-anlaytics directory if you are working through the consummate Bootcamp course equally a part of our Professional Certificate program.
To make sure you did things right, in bash, cd to the exercise-git-skillz directory on your calculator. Blazon:
$ git remote -five
The paths returned should await something like this:
https://github.com/your-username/practice-git-skillz
Source: https://www.earthdatascience.org/courses/intro-to-earth-data-science/git-github/version-control/fork-clone-github-repositories/
Post a Comment for "How to Download Github Repository Then Upload"